Ultrasound
What is an ultrasound?
Ultrasound is the term used for high-frequency sound waves. Ultrasound examinations use these sound waves to produce a picture or image onto a screen showing the inside of your body.
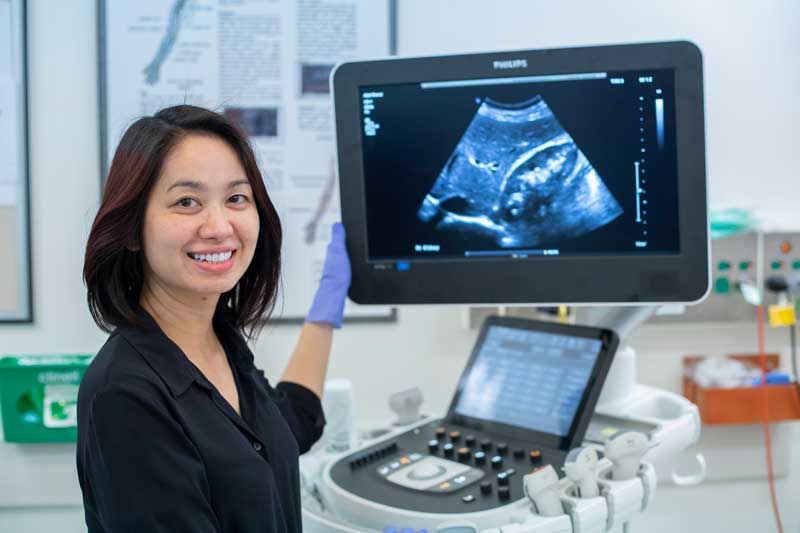
An ultrasound is carried out by a trained health professional (sonographer or radiologist) using a smooth, hand-held device called a transducer that they move across the body with a sliding and rotating action. The transducer transmits the high-frequency sound waves into your body. Different sound waves are reflected from different soft tissue, structures or parts in the body in different ways. These sound waves are converted to electrical impulses that produce a moving image displayed on a screen.
An ultrasound has many advantages. It is painless and does not use radiation, which means it is very safe. There are no injections unless your doctor has specifically requested one. The high-frequency sound waves ensure images show very high detail, capable of looking at the very tiniest parts of the body. Ultrasound can be carried out while there is movement, so it is excellent for the imaging of babies and children.
A health professional will be there with you, and you have the opportunity to communicate any concerns you have.
Transvaginal ultrasound
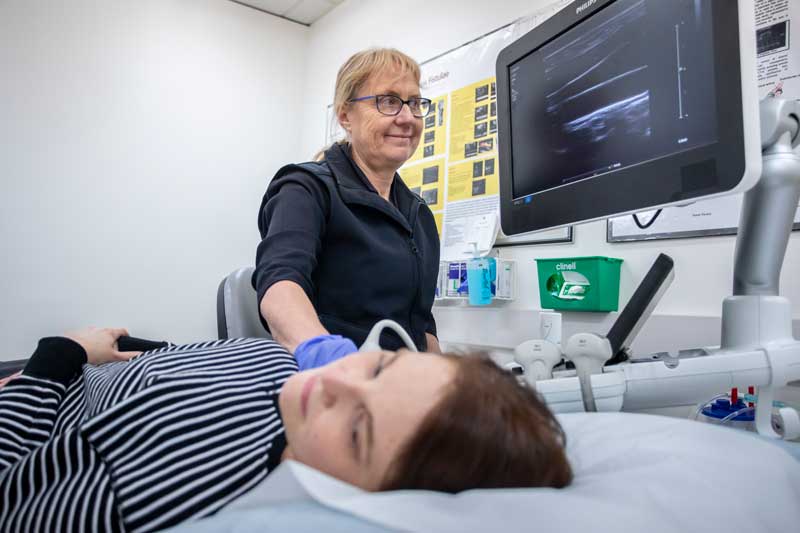
Transvaginal ultrasound is used to look at the female pelvis area. It looks at the pelvic organs from inside the vagina using a special smooth, thin, handheld device called a transducer. It helps by showing if there is anything unusual in the uterus (womb), cervix (the neck of the womb), endometrium (lining of the womb), fallopian tubes, ovaries, bladder or the pelvic cavity.
This differs from an abdominal ultrasound, which uses a warm water-based clear gel applied to the skin of the abdomen and the transducer is moved gently across the pelvic area.
All ultrasound transducers transmit high-frequency sound waves, and these are reflected from different soft tissue, structures or parts in the body in different ways. These sound waves are converted to electrical impulses that produce a moving image on a screen.
