Referral to emergency
If any of the following are present or suspected, please refer the patient to the emergency department (via ambulance if necessary) or seek emergent medical advice if in a remote region.
- Systemic features including:
- febrile greater than 380
- haemodynamic instability
- positive blood cultures
- rising or unchanging CRP
- hypotension
- tachycardia
- concern for deep tissue infection (presence of bullae, necrosis, or subcutaneous emphysema)
- rapidly progressive infection
- lack of systemic or local response to oral antibiotics
- not all urgent assessments require presentation to the emergency department. Please contact the plastic service to discuss your concerns via switchboard.
For clinical advice, please telephone the relevant specialty service.
Central Adelaide Local Health Network
- Royal Adelaide Hospital (08) 7074 0000
- The Queen Elizabeth Hospital (08) 8222 6000
Southern Adelaide Local Health Network
- Flinders Medical Centre (08) 8204 5511
Exclusions
- stage 1/2 pressure injury
Triage categories
Category 1 - appointment clinically indicated within 30 days
- pressure injury stage 3/4 without systemic features or rapidly progressing infection
- pressure injury with concerns of osteomyelitis
- rapidly deteriorating or advancing pressure injury
All category 1 referrals please consider discussing with on call registrar prior to referring to ensure timely review
Category 2 — appointment clinically indicated within 90 days
- any pressure injury of concern - after discussion with on call Plastic and Reconstructive Registrar
Category 3 — appointment clinically indicated within 365 days
- long standing stage 3/4 pressure injury for consideration of reconstruction
Essential referral information
Completion required before first appointment to ensure patients are ready for care. Please indicate in the referral if the patient is unable to access mandatory tests or investigations as they incur a cost or are unavailable locally.
- past medical/surgical history
- current medication list – especially immunosuppressants; steroids, noacs or warfarin
- allergies and sensitivities – including topical application/dressings
- social/living situation
- mobility including:
- assistance if required
- frequency of mobilisation per day, e.g. house bound, walks to letter box and back, sleeps in recliner
- mobility aids
- cognitive impairment
- continence faecal/urinary and aids
- occupational therapist, physiotherapist, dietician assessments/reports – where concerns of increasing deconditioning and inadequate community support exist
- treatment or management trialled including:
- offloading strategies and management plan
- adherence to management plan
- community services in place and current management plan e.g. Metropolitan Referral Unit visits 3 times a week with a copy of current dressing management plan
- clinical assessment of wounds including:
- T.I.M.E assessment tool
- duration and recurrence
- microscopy, culture and sensitivity (MCS) if clinical infection present e.g. malodorous, purulent discharge or collection, increasing redness, swelling, pain
- for lower limb involvement:
- presence of pulses
- ankle/brachial pressure index (ABPI) completed
Additional information to assist triage categorisation
- pathology (less than 12 weeks old)
- complete blood examination (CBE)
- urea, electrolytes, creatinine (UEC)
- liver function test (LFT)
- HbA1C% (diabetics)
- c-reactive protein (CRP)
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
- photograph including disposable measurement tool – with patient’s consent, where secure image transfer, identification and storage is possible
Clinical management advice
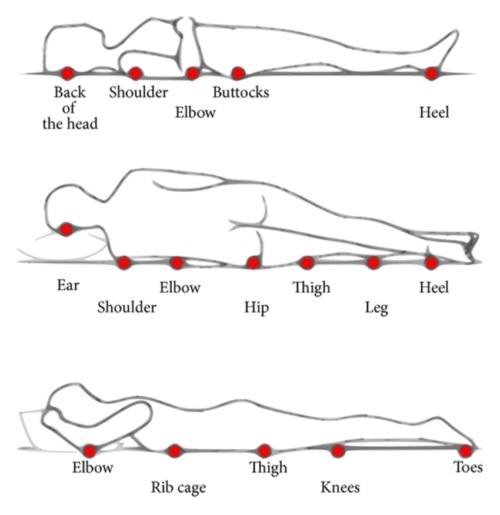
The most common locations of pressure injury locations are:
- back of the head
- shoulder blades
- elbow
- coccyx (tail bone)
- heels
- ear
- side of shoulder
- pelvis
- hip
- malleolous (ankle bone)
Offloading affected area will enable wound healing to begin.
There is an expectation that all people referred for pressure injury management are required to participate in any offloading and pressure reduction recommendations.
Where pressure injuries are present on feet/Achilles examine for evidence of the following and consider high-risk foot referral:
- neuropathy
- diabetes mellitus
- ulceration
- callus
- infection and/or inflammation
- deformity
- gangrene
- non-active Charcot arthropathy
- peripheral pulses foot/ankle/calf
Pressure injuries related to a pre-existing disability will require complex management planning and coordination with NDIS case managers, especially with relation to metropolitan or country referral unit involvement.
Clinical resources
- Pan Pacific Pressure Injury Alliance – Prevention and Treatment of Pressure Ulcers/Injuries: Clinical Practice Guideline: The International Guideline
- SA Health - Country Referral Unit
- SA Health - Metropolitan Referral Unit
- Therapeutic Guidelines (eTG) - Assessing Patients With an Ulcer or Wound
- eTG - Factors Affecting Ulcer and Wound Healing
- eTG - Pressure Injuries
Reason for request
- to establish a diagnosis
- for treatment or intervention
- for advice and management
- for specialist to take over management
- for a specified test/investigation the General Practitioner cannot order
- for other reason (e.g. rapidly accelerating disease progression)
- transfer of care from another tertiary service
- clinical judgement indicates a referral for specialist review is necessary.
Patient demographic details
- full name, including aliases
- date of birth
- residential and postal address
- telephone contact number/s – home, mobile and alternative
- Medicare number, where eligible
- name of the parent or caregiver, if appropriate
- preferred language and interpreter requirements
- identifies as Aboriginal and/or Torres Strait Islander
Clinical modifiers
- impact on employment
- impact on education
- impact on home
- impact on activities of daily living
- impact on ability to care for others
- impact on personal frailty or safety
- identifies as Aboriginal and/or Torres Strait Islander
Other relevant information
- Willingness to have surgery, where surgery is a likely intervention.
- Choice to be treated as a public or private patient.
- Compensable status, e.g. DVA, Work Cover, Motor Vehicle Insurance, etc.
- Relevant social history, including identifying if you feel your patient is from a vulnerable population, under guardianship/out-of-home care arrangements and/or requires a third party to receive correspondence on their behalf.
- Triage of a specialist outpatient referral is based on clinical decision making to allocate an appropriate urgency categorisation.
- Where appropriate and where available, the referral may be streamed to an associated public allied health and/or nursing service. Access to some specific services may include initial assessment and management by associated public allied health and/or nursing, which may either facilitate or negate the need to see the public medical specialist.
- A change in patient circumstance (such as condition deteriorating or pregnancy) may affect the urgency categorisation and should be communicated as soon as possible.
- All new referrals will be triaged by a consultant and appointment times scheduled according to clinical urgency.