PDF 78 KB
Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease is caused by the Coxsackie A virus. Spread takes place through contact with the fluid in the blisters.
Hand, foot and mouth disease is a viral infection usually caused by the Coxsackie virus group A. However, sometimes it is caused by other viruses such as an echovirus or an enterovirus. Enterovirus 71 (EV71) can cause hand, foot and mouth disease as well as more serious illness, particularly in children.
The virus can spread from an infected person by:
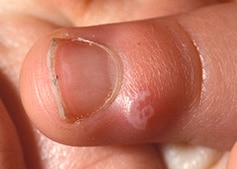 Symptoms may include:
Symptoms may include:
Affected young children may refuse to eat or drink.
Image courtesy Prof. David Gordon, Flinders Medical Centre, Adelaide, South Australia.
Diagnosis is usually made when seeing a doctor. Laboratory tests are not usually required.
(time between becoming infected and developing symptoms)
3 to 5 days.
(time during which an infected person can infect others)
The blisters are infectious as long as they contain fluid. The faeces can remain infectious for several weeks.
Usually no specific treatment is required. Use of paracetamol for the fever and any discomfort may be indicated. Aspirin should not be given to children under 12 years of age unless specifically recommended by a doctor.